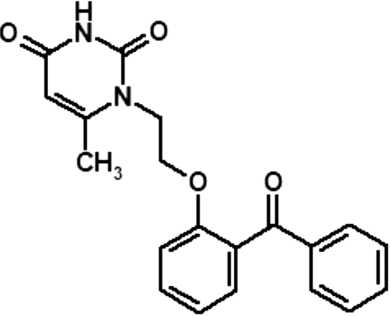
Study of the specific toxic effects of the substance 1-[2-(2-benzoylphenoxy)ethyl]-6-methyluracil, the original non-nucleoside inhibitor of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (Retroviridae; Orthoretrovirinae; Lentivirus: Human immunodeficiency virus 1) reverse transcriptase
- Authors: Gaidai E.A.1, Kryshen K.L.1, Jain (Korsakova) E.A.2, Demchenko D.V.3, Kargopol’tseva D.R.1, Katel’nikova A.E.1, Gaidai D.S.1, Balabanyan V.Y.2
-
Affiliations:
- «RMC HOME OF PHARMACY» JSC
- FSBEI HE «Lomonosov Moscow State University»
- CJSC «St. Petersburg Institute of Pharmacy»
- Issue: Vol 66, No 4 (2021)
- Pages: 279-288
- Section: ORIGINAL RESEARCHES
- URL: https://journal-vniispk.ru/0507-4088/article/view/118185
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.36233/0507-4088-59
- ID: 118185
Cite item
Full Text
Abstract
Introduction. Combination antiretroviral therapy is currently the main component of treatment for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infected patients. At the same time, the high mutational potential of the virus and the frequency of side effects of existing drugs dictate the need for the development and preclinical study of new, more effective and safer compounds.
The aim of the study is to evaluate the specific types of toxicity of a new non-nucleoside inhibitor of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) reverse transcriptase (RNA-dependent DNA revertase) (NNRTI) based on the substance 1-[2-(2-benzoylphenoxy)ethyl]-6-methyluracil, a benzophenone derivative.
Material and methods. The study investigated reproductive toxicity, embryotoxicity, immunotoxicity, genotoxic (in micronucleus test in and comet assay) and allergenic properties of the test itemcompound. It was tested on three species of animals in two doses: the estimated therapeutic dose (1 TD) and its tenfold equivalent (10 TD). Taking into account the metabolic coefficients, the doses for rats (Rattus) were 9 and 90 mg/kg, for mice (Mus musculus), 21 and 210 mg/kg, and for guinea pigs (Cavia porcellus), 8 and 80 mg/kg, respectively.
Results and discussion. According to the obtained results, a favorable safety profile of the tested compound was established. Negative effects on the immune system, reproductive function, the body of pregnant animals and the fetus were not observed, as well as the compound did not have genotoxic and allergenic properties.
Conclusion. These data allows to consider the studied compound as a promising therapeutic candidate for the treatment of HIV-1 infection.
Full Text
##article.viewOnOriginalSite##About the authors
E. A. Gaidai
«RMC HOME OF PHARMACY» JSC
Email: fake@neicon.ru
ORCID iD: 0000-0002-5295-6384
188663, Leningrad Region, Kuz’molovsky vill., Russia
Russian FederationK. L. Kryshen
«RMC HOME OF PHARMACY» JSC
Author for correspondence.
Email: kryshen.kl@doclinika.ru
ORCID iD: 0000-0003-1451-7716
Kryshen’ K.L., Ph.D. (Biol.), Head of the Toxicology and Microbiology Department.
188663, Leningrad Region, Kuz’molovsky vill., Russia
Russian FederationE. A. Jain (Korsakova)
FSBEI HE «Lomonosov Moscow State University»
Email: fake@neicon.ru
ORCID iD: 0000-0003-0283-8598
119991, Moscow, Russia
Russian FederationD. V. Demchenko
CJSC «St. Petersburg Institute of Pharmacy»
Email: fake@neicon.ru
ORCID iD: 0000-0003-3856-3936
188663, Leningrad Region, Kuz’molovsky vill., Russia
Russian FederationD. R. Kargopol’tseva
«RMC HOME OF PHARMACY» JSC
Email: fake@neicon.ru
ORCID iD: 0000-0002-9944-5223
188663, Leningrad Region, Kuz’molovsky vill., Russia
Russian FederationA. E. Katel’nikova
«RMC HOME OF PHARMACY» JSC
Email: fake@neicon.ru
ORCID iD: 0000-0003-3203-9869
188663, Leningrad Region, Kuz’molovsky vill., Russia
Russian FederationD. S. Gaidai
«RMC HOME OF PHARMACY» JSC
Email: fake@neicon.ru
ORCID iD: 0000-0002-8773-5717
188663, Leningrad Region, Kuz’molovsky vill., Russia
Russian FederationV. Yu. Balabanyan
FSBEI HE «Lomonosov Moscow State University»
Email: fake@neicon.ru
ORCID iD: 0000-0002-5744-7060
119991, Moscow, Russia
Russian FederationReferences
- ВИЧ/СПИД в мире. Available at: http://aids-centr.perm.ru/Статистика/ВИЧ/СПИД-в-мире (accessed August 8, 2021).
- Озеров А.А. Пиримидиновые ненуклеозидные ингибиторы обратной транскриптазы ВИЧ-1 – история разработки и перспективы. Вестник Волгоградского государственного медицинско- го университета. 2012; (3): 10–7.
- Novikov M.S., Ivanova O.N., Ivanov A.V., Ozerov A.A., Valuev-Elliston V.T., Temburnikar K., et al. 1-[2-(2-Benzoyl- and 2-benzylphenoxy) ethyl]uracils as potent anti-HIV-1 agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011; 19(19): 5794–802.
- Озеров А.А., Новиков М.С., Луганченко А.И., Хартман Т., Букхайт Р.У. Новые N-[2-(Бензоилфенокси)этил]производные нуклеиновых оснований – синтез и анти-ВИЧ-1 активность in vitro. Волгоградский научно-медицинский журнал. 2012; (4): 15–8.
- Директива 2010/63/EU Европейского парламента и Совета Европейского союза по охране животных, используемых в научных целях. СПб.; 2012.
- Миронов А.Н., ред. Руководство по доклиническим исследованиям лекарственных средств. M.; 2012.
- OECD Guidelines for testing of chemicals. Test No. 414: Prenatal Developmental Toxicity Study. Available at: https://www.oecdilibrary.org/environment/test-no-414-prenatal-developmenttoxicity-study_9789264070820-en (accessed August 8, 2021).
- OECD Guideline for the testing of chemicals. Test No. 415: One- Generation Reproduction Toxicity Study. Available at: https://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/environment/test-no-415-one-generationreproduction-toxicity-study_9789264070844-en (accessed August 8, 2021).
- OECD Guideline for the testing of chemicals. Test No. 474: Mammalian Erythrocyte Micronucleus test. Available at: https://www.oecd.org/env/test-no-474-mammalian-erythrocytemicronucleus-test-9789264264762-en.htm (accessed August 8, 2021).
- OECD Guideline for the testing of chemicals. Test No. 489: In Vivo Mammalian Alkaline Comet Assay. Available at: https://www.oecdilibrary.org/environment/test-no-489-in-vivo-mammalian-alkalinecomet-assay_9789264264885-en (accessed August 8, 2021).
- Weigle W.O., Cochrane C.G., Dixon F.J. Anaphylactogenic properties of soluble antigen-antibody complexes in the guinea pig and rabbit. J. Immunol. 1960; 85: 469–77.
Supplementary files