Применение радиомики при заболеваниях костно-мышечной системы: научный обзор
- Авторы: Плешков М.О.1, Замышевская М.А.1, Кучинский Е.В.1, Jin X.2, Zhang J.2, Завадовская В.Д.1, Зоркальцев М.А.1, Ким Т.В.1, Погонченкова Д.А.1, Удодов В.Д.1, Толмачев И.В.1
-
Учреждения:
- Сибирский государственный медицинский университет
- 1st Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University
- Выпуск: Том 6, № 1 (2025)
- Страницы: 78-96
- Раздел: Обзоры
- URL: https://journal-vniispk.ru/DD/article/view/310054
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17816/DD633978
- ID: 310054
Цитировать
Аннотация
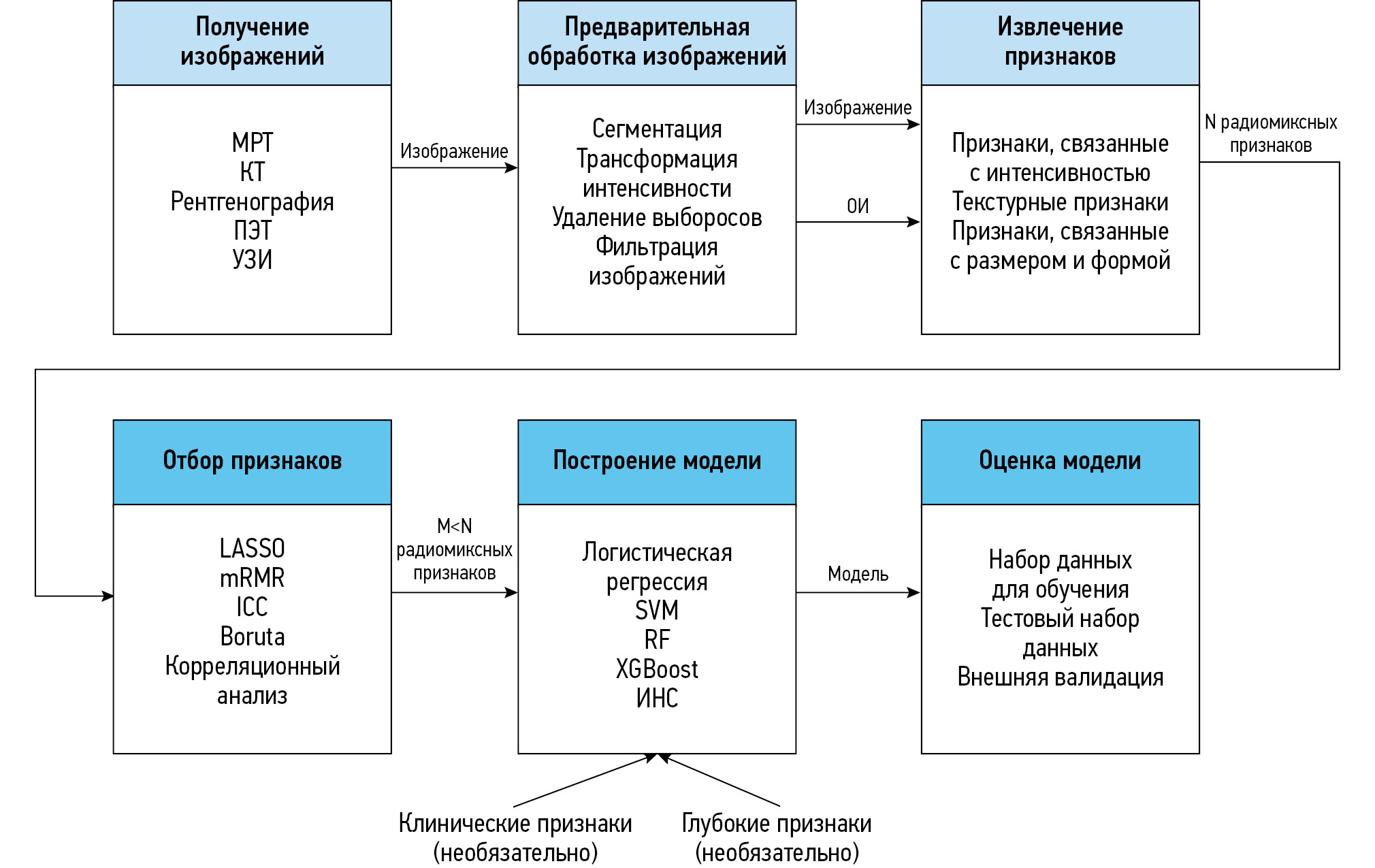
Радиомика — это методика извлечения различных количественных признаков из цифровых медицинских изображений. Десять лет назад сфера её применения ограничивалась только онкологией, однако сейчас радиомиксный анализ используют также в диагностике заболеваний другого профиля, в частности болезней костно-мышечной системы и соединительной ткани. В статье представлен обзор актуальных исследований в области радиомики, которые используют с целью диагностики заболеваний костно-мышечной системы.
В обзор включены оригинальные научные статьи (n=37), опубликованные на английском языке в период с 2020 по 2023 год. Среди наиболее распространённых методов медицинской визуализации выделены магнитно-резонансная и компьютерная томография — 54 и 32% соответственно. Реже использовали двухэнергетическую рентгеновскую абсорбциометрию, ультразвуковое исследование и рентгенографию — 14, 5 и 5% соответственно. В большинстве исследований для выявления областей интереса применяли ручную сегментацию. На основе клинических, радиомиксных и глубоких признаков разработаны различные модели, наиболее распространёнными из которых являются смешанные — клинико-радиомиксные модели. При заболеваниях костно-мышечной системы чаще всего наблюдают поражения позвоночника и крупных суставов.
Мультимодальные радиомиксные модели, созданные с помощью нескольких источников данных (в основном клиникорадиомиксных), применяют в диагностике болезней костно-мышечной системы чаще, чем мономодальные — на основе одного источника (только клинические или радиомиксные признаки). Данный факт можно объяснить большей проработанностью классификации, вероятно, по причине включения большего числа независимых источников информации. Несмотря на перспективность разработки таких моделей и технологий глубокого обучения для автоматической сегментации и классификации изображений, значительных усилий требует формирование баз изображений для их глубокого обучения. В этом смысле особенно целесообразно применять радиомику с целью раннего выявления заболеваний костно-мышечной системы, не имеющих отчётливых и специфичных визуальных симптомов при дебюте патологического процесса.
Полный текст
Открыть статью на сайте журналаОб авторах
Максим Олегович Плешков
Сибирский государственный медицинский университет
Автор, ответственный за переписку.
Email: maksim.o.pleshkov@gmail.com
ORCID iD: 0000-0002-4131-0115
SPIN-код: 8625-0940
Россия, Томск
Мария Александровна Замышевская
Сибирский государственный медицинский университет
Email: zamyshevskayamari@mail.ru
ORCID iD: 0000-0001-7582-3843
SPIN-код: 4434-1179
канд. мед. наук
Россия, ТомскЕгор Владиславович Кучинский
Сибирский государственный медицинский университет
Email: egorelsigich@gmail.com
ORCID iD: 0009-0002-5960-0935
Россия, Томск
Xiance Jin
1st Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University
Email: jinxc1979@hotmail.com
ORCID iD: 0000-0002-4117-5953
Китай, Вэньчжоу
Ji Zhang
1st Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University
Email: jizhang1996@126.com
ORCID iD: 0000-0002-2718-6509
Китай, Вэньчжоу
Вера Дмитриевна Завадовская
Сибирский государственный медицинский университет
Email: wdzav@mail.ru
ORCID iD: 0000-0001-6231-7650
SPIN-код: 7905-8363
д-р мед. наук
Россия, ТомскМаксим Александрович Зоркальцев
Сибирский государственный медицинский университет
Email: zorkaltsev@mail.ru
ORCID iD: 0000-0003-0025-2147
SPIN-код: 3769-8560
д-р мед. наук
Россия, ТомскТхе Ван Ким
Сибирский государственный медицинский университет
Email: Pavel.kim.08@mail.ru
ORCID iD: 0009-0002-9766-6986
SPIN-код: 7834-9024
Россия, Томск
Дарья Александровна Погонченкова
Сибирский государственный медицинский университет
Email: azarova_d_a@mail.ru
ORCID iD: 0000-0002-5903-3662
SPIN-код: 4141-9068
канд. мед. наук
Россия, ТомскВладимир Дмитриевич Удодов
Сибирский государственный медицинский университет
Email: linx86rus@gmail.com
ORCID iD: 0000-0002-1321-7861
SPIN-код: 3619-0496
канд. мед. наук
Россия, ТомскИван Владиславович Толмачев
Сибирский государственный медицинский университет
Email: ivantolm@mail.ru
ORCID iD: 0000-0002-2888-5539
SPIN-код: 1074-1268
канд. мед. наук
Россия, ТомскСписок литературы
- Wolbarst AB, Capasso P, Wyant AR. Medical imaging: essentials for physicians. New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons; 2013. doi: 10.1002/9781118480267
- Shaikh F, Franc B, Allen E, et al. Translational radiomics: defining the strategy pipeline and considerations for application — Part 1: from methodology to clinical implementation. Journal of the American College of Radiology. 2018;15(3):538–542. doi: 10.1016/j.jacr.2017.12.008
- Acharya UR, Hagiwara Y, Sudarshan VK, et al. Towards precision medicine: from quantitative imaging to radiomics. Journal of Zhejiang University-SCIENCE B. 2018;19(1):6–24. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B1700260 EDN: YEROEH
- Giardino A, Gupta S, Olson E, et al. Role of imaging in the era of precision medicine. Academic Radiology. 2017;24(5):639–649. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2016.11.021 EDN: YXQFYH
- Hatt M, Le Rest CC, Tixier F, et al. Radiomics: Data Are Also Images. Journal of Nuclear Medicine. 2019;60(Suppl. 2):38S–44S. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.118.220582
- Lambin P, Rios-Velazquez E, Leijenaar R, et al. Radiomics: extracting more information from medical images using advanced feature analysis. European Journal of Cancer. 2012;48(4):441–446. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2011.11.036
- Keek SA, Leijenaar RTH, Jochems A, Woodruff HC. A review on radiomics and the future of theranostics for patient selection in precision medicine. The British Journal of Radiology. 2018;91(1091):20170926. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20170926
- Scapicchio C, Gabelloni M, Barucci A, et al. A deep look into radiomics. La radiologia medica. 2021;126(10):1296–1311. doi: 10.1007/s11547-021-01389-x EDN: CFTFXK
- Lambin P, Leijenaar RTH, Deist TM, et al. Radiomics: the bridge between medical imaging and personalized medicine. Nature Reviews Clinical Oncology. 2017;14(12):749–762. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2017.141
- Zhang X, Zhang Y, Zhang G, et al. Deep learning with radiomics for disease diagnosis and treatment: challenges and potential. Frontiers in Oncology. 2022;12:773840. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.773840 EDN: HKEDBO
- Weng W, Zhu X. INet: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. IEEE Access. 2021;9:16591–16603. doi: 10.1109/access.2021.3053408 EDN: TKNUNY
- Demircioğlu A. Are deep models in radiomics performing better than generic models? A systematic review. European Radiology Experimental. 2023;7(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s41747-023-00325-0
- McCague C, Ramlee S, Reinius M, et al. Introduction to radiomics for a clinical audience. Clinical Radiology. 2023;78(2):83–98. doi: 10.1016/j.crad.2022.08.149 EDN: FTQEEU
- Davis KW, Blankenbaker DG, Bernard S. Diagnostic imaging: musculoskeletal non-traumatic disease. 3rd ed. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 2022.
- Liu S, Wang B, Fan S, et al. Global burden of musculoskeletal disorders and attributable factors in 204 countries and territories: a secondary analysis of the Global Burden of Disease 2019 study. BMJ Open. 2022;12(6):e062183. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2022-062183 EDN: JPFMCK
- Jiang YW, Xu XJ, Wang R, Chen CM. Radiomics analysis based on lumbar spine CT to detect osteoporosis. European Radiology. 2022;32(11):8019–8026. doi: 10.1007/s00330-022-08805-4 EDN: FFIEJM
- Lim HK, Ha HI, Park SY, Han J. Prediction of femoral osteoporosis using machine-learning analysis with radiomics features and abdomen-pelvic CT: a retrospective single center preliminary study. PLOS ONE. 2021;16(3):e0247330. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0247330 EDN: BXSLMY
- Xue Z, Huo J, Sun X, et al. Using radiomic features of lumbar spine CT images to differentiate osteoporosis from normal bone density. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders. 2022;23(1):1–9. doi: 10.1186/s12891-022-05309-6 EDN: QMPUNB
- Xue Z, Wang L, Sun Q, et al. Radiomics analysis using MR imaging of subchondral bone for identification of knee osteoarthritis. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research. 2022;17(1):1–11. doi: 10.1186/s13018-022-03314-y EDN: MUEEVI
- Hirvasniemi J, Klein S, Bierma-Zeinstra S, et al. A machine learning approach to distinguish between knees without and with osteoarthritis using MRI-based radiomic features from tibial bone. European Radiology. 2021;31(11):8513–8521. doi: 10.1007/s00330-021-07951-5 EDN: OQYJMS
- Yu K, Ying J, Zhao T, et al. Prediction model for knee osteoarthritis using magnetic resonance–based radiomic features from the infrapatellar fat pad: data from the osteoarthritis initiative. Quantitative Imaging in Medicine and Surgery. 2023;13(1):352–369. doi: 10.21037/qims-22-368 EDN: XMHHBS
- Colelli G, Barzaghi L, Paoletti M, et al. Radiomics and machine learning applied to STIR sequence for prediction of quantitative parameters in facioscapulohumeral disease. Frontiers in Neurology. 2023;14:1105276. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1105276 EDN: TFSEOI
- Zhang MZ, Ou-Yang HQ, Jiang L, et al. Optimal machine learning methods for radiomic prediction models: clinical application for preoperative T2*-weighted images of cervical spondylotic myelopathy. JOR SPINE. 2021;4(4):e1178. doi: 10.1002/jsp2.1178 EDN: QCNMEY
- Çorbacıoğlu ŞK, Aksel G. Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis in diagnostic accuracy studies: a guide to interpreting the area under the curve value. Turkish Journal of Emergency Mededicine. 2023;23(4):195–198. doi: 10.4103/tjem.tjem_182_23
- Chun KJ. Bone densitometry. Seminars in Nuclear Medicine. 2011;41(3):220–228. doi: 10.1053/j.semnuclmed.2010.12.002 EDN: XZBHAJ
- Yao Q, Liu M, Yuan K, et al. Radiomics nomogram based on dual-energy spectral CT imaging to diagnose low bone mineral density. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders. 2022;23(1):1–10. doi: 10.1186/s12891-022-05389-4 EDN: ZJCBIU
- Dai H, Wang Y, Fu R, et al. Radiomics and stacking regression model for measuring bone mineral density using abdominal computed tomography. Acta Radiologica. 2021;64(1):228–236. doi: 10.1177/02841851211068149 EDN: KCQOEI
- Rastegar S, Vaziri M, Qasempour Y, et al. Radiomics for classification of bone mineral loss: a machine learning study. Diagnostic and Interventional Imaging. 2020;101(9):599–610. doi: 10.1016/j.diii.2020.01.008 EDN: MXTTFU
- Tenório APM, Ferreira-Junior JR, Dalto VF, et al. Radiomic quantification for MRI assessment of sacroiliac joints of patients with spondyloarthritis. Journal of Digital Imaging. 2022;35(1):29–38. doi: 10.1007/s10278-021-00559-7 EDN: EDSNBE
- Xie Q, Chen Y, Hu Y, et al. Development and validation of a machine learning-derived radiomics model for diagnosis of osteoporosis and osteopenia using quantitative computed tomography. BMC Medical Imaging. 2022;22(1):1–9. doi: 10.1186/s12880-022-00868-5 EDN: TBGMNV
- Wang J, Zhou S, Chen S, et al. Prediction of osteoporosis using radiomics analysis derived from single source dual energy CT. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders. 2023;24(1):100. doi: 10.1186/s12891-022-06096-w EDN: CSYYUO
- Huang CB, Hu JS, Tan K, et al. Application of machine learning model to predict osteoporosis based on abdominal computed tomography images of the psoas muscle: a retrospective study. BMC Geriatrics. 2022;22(1):796. doi: 10.1186/s12877-022-03502-9
- He L, Liu Z, Liu C, et al. Radiomics based on lumbar spine magnetic resonance imaging to detect osteoporosis. Academic Radiology. 2021;28(6):e165–e171. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2020.03.046 EDN: UHSGDH
- Zhao Y, Zhao T, Chen S, et al. Fully automated radiomic screening pipeline for osteoporosis and abnormal bone density with a deep learning-based segmentation using a short lumbar mDixon sequence. Quantitative Imaging in Medicine and Surgery. 2022;12(2):1198–1213. doi: 10.21037/qims-21-587 EDN: NZYATO
- Kutsal FY, Ergin Ergani GO. Vertebral compression fractures: Still an unpredictable aspect of osteoporosis. Turkish Journal of Medical Sciences. 2021;51(2):393–399. doi: 10.3906/sag-2005-315 EDN: YTBYNY
- Wang M, Chen X, Cui W, et al. A computed tomography-based radiomics nomogram for predicting osteoporotic vertebral fractures: a longitudinal study. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. 2022;108(6):e283–e294. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgac722 EDN: ZDBNTO
- Ge C, Chen Z, Lin Y, et al. Preoperative prediction of residual back pain after vertebral augmentation for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: initial application of a radiomics score based nomogram. Frontiers in Endocrinology. 2022;13:1093508. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1093508 EDN: SHBOCJ
- Yang H, Yan S, Li J, et al. Prediction of acute versus chronic osteoporotic vertebral fracture using radiomics-clinical model on CT. European Journal of Radiology. 2022;149:110197. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2022.110197 EDN: HVGSBS
- Biamonte E, Levi R, Carrone F, et al. Artificial intelligence-based radiomics on computed tomography of lumbar spine in subjects with fragility vertebral fractures. Journal of Endocrinological Investigation. 2022;45(10):2007–2017. doi: 10.1007/s40618-022-01837-z EDN: EAIWLD
- Erdes ShF, Badokin VV, Bochkova AG, et al. On the terminology of spondyloarthritis. Rheumatology Science and Practice. 2015;53(6):657–660. doi: 10.14412/1995-4484-2015-657-660 EDN: WYDFJB
- Ramiro S, Nikiphorou E, Sepriano A, et al. ASAS-EULAR recommendations for the management of axial spondyloarthritis: 2022 update. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. 2023;82(1):19–34. doi: 10.1136/ard-2022-223296 EDN: DLBUZY
- Ye L, Miao S, Xiao Q, et al. A predictive clinical-radiomics nomogram for diagnosing of axial spondyloarthritis using MRI and clinical risk factors. Rheumatology. 2021;61(4):1440–1447. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keab542 EDN: FELRLG
- Tenório APM, Faleiros MC, Junior JRF, et al. A study of MRI-based radiomics biomarkers for sacroiliitis and spondyloarthritis. International Journal of Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery. 2020;15(10):1737–1748. doi: 10.1007/s11548-020-02219-7 EDN: RLWIQG
- Zheng M, Miao S, Chen D, et al. Can radiomics replace the SPARCC scoring system in evaluating bone marrow edema of sacroiliac joints in patients with axial spondyloarthritis? Clinical Rheumatology. 2023;42(6):1675–1682. doi: 10.1007/s10067-023-06543-6 EDN: FHQBFF
- Maksymowych WP, Mallon C, Morrow S, et al. Development and validation of the spondyloarthritis research consortium of canada (SPARCC) enthesitis index. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. 2009;68(6):948–953. doi: 10.1136/ARD.2007.084244
- Lacerda C, Linhas R, Duarte R. Tuberculous spondylitis: a report of different clinical scenarios and literature update. Case Reports in Medicine. 2017;2017:1–4. doi: 10.1155/2017/4165301
- Wu S, Wei Y, Li H, et al. A predictive clinical-radiomics nomogram for differentiating tuberculous spondylitis from pyogenic spondylitis using CT and clinical risk factors. Infection and Drug Resistance. 2022;15:7327–7338. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S388868 EDN: TBVWYF
- Yu G, Yang W, Zhang J, et al. Application of a nomogram to radiomics labels in the treatment prediction scheme for lumbar disc herniation. BMC Medical Imaging. 2022;22(1):51. doi: 10.1186/s12880-022-00778-6 EDN: WCRFUE
- Song M, Yang H, Yang H, et al. MR imaging radiomics analysis based on lumbar soft tissue to evaluate lumbar fascia changes in patients with low back pain. Academic Radiology. 2023;30(11):2450–2457. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2023.02.038 EDN: UWOCTW
- Klontzas ME, Manikis GC, Nikiforaki K, et al. Radiomics and machine learning can differentiate transient osteoporosis from avascular necrosis of the hip. Diagnostics. 2021;11(9):1686. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11091686 EDN: WCRMFH
- Kim S, Kim BR, Chae HD, et al. Deep radiomics–based approach to the diagnosis of osteoporosis using hip radiographs. Radiology: Artificial Intelligence. 2022;4(4):e210212. doi: 10.1148/ryai.210212 EDN: QKWOZX
- Castañeda S, Roman-Blas JA, Largo R, Herrero-Beaumont G. Subchondral bone as a key target for osteoarthritis treatment. Biochemical Pharmacology. 2012;83(3):315–323. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2011.09.018
- Lin T, Peng S, Lu S, et al. Prediction of knee pain improvement over two years for knee osteoarthritis using a dynamic nomogram based on MRI-derived radiomics: a proof-of-concept study. Osteoarthritis and Cartilage. 2023;31(2):267–278. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2022.10.014 EDN: HEPKTM
- Xie Y, Dan Y, Tao H, et al. Radiomics feature analysis of cartilage and subchondral bone in differentiating knees predisposed to posttraumatic osteoarthritis after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction from healthy knees. BioMed Research International. 2021;2021(1):4351499. doi: 10.1155/2021/4351499 EDN: GEGKRA
- Sander R. Asymptomatic osteoporosis masks the importance of taking medication. Nursing Older People. 2007;19(10):23–23. doi: 10.7748/nop.19.10.23.s21
- Li W, Feng J, Zhu D, et al. Nomogram model based on radiomics signatures and age to assist in the diagnosis of knee osteoarthritis. Experimental Gerontology. 2023;171:112031. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2022.112031 EDN: OJHMQD
- Valesan LF, Da-Cas CD, Réus JC, et al. Prevalence of temporomandibular joint disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clinical Oral Investigations. 2021;25(2):441–453. doi: 10.1007/s00784-020-03710-w EDN: LUZGIY
- Orhan K, Driesen L, Shujaat S, et al. Development and validation of a magnetic resonance imaging-based machine learning model for TMJ pathologies. BioMed Research International. 2021;2021(1):6656773. doi: 10.1155/2021/6656773 EDN: IKONFS
- Muraoka H, Kaneda T, Hirahara N, et al. Magnetic resonance image texture analysis of the lateral pterygoid muscle in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a preliminary report. Oral Radiology. 2022;39(2):242–247. doi: 10.1007/s11282-022-00625-y EDN: ZDPFQW
- Ricardo ALF, da Silva GA, Ogawa CM, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging texture analysis for quantitative evaluation of the mandibular condyle in juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Oral Radiology. 2022;39(2):329–340. doi: 10.1007/s11282-022-00641-y EDN: LWUNPK
- Wang L, Wen D, Yin Y, et al. Musculoskeletal ultrasound image-based radiomics for the diagnosis of achilles tendinopathy in skiers. Journal of Ultrasound in Medicine. 2022;42(2):363–371. doi: 10.1002/jum.16059 EDN: RFSUOT
- Gulani V, Seiberlich N. Quantitative MRI: rationale and challenges. In: Seiberlich N, Gulani V, Calamante F, editors. Quantitative magnetic resonance imaging. London: Elsevier; 2020. P. xxxvii–li. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-817057-1.00001-9
- Jiang H, Chen L, Zhao Y, et al. Machine learning-based ultrasomics for predicting subacromial impingement syndrome stages. Journal of Ultrasound in Medicine. 2021;41(9):2279–2285. doi: 10.1002/jum.15914 EDN: YEOHCZ
- Yin R, Jiang M, Lv WZ, et al. Study processes and applications of ultrasomics in precision medicine. Frontiers in Oncology. 2020;10:1736. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.01736 EDN: QZLABO
- AL Qurri A, Almekkawy M. Improved UNet with attention for medical image segmentation. Sensors. 2023;23(20):8589. doi: 10.3390/s23208589 EDN: KNTAZU
- Bach Cuadra M, Favre J, Omoumi P. Quantification in musculoskeletal imaging using computational analysis and machine learning: segmentation and radiomics. Seminars in Musculoskeletal Radiology. 2020;24(1):50–64. doi: 10.1055/s-0039-3400268 EDN: KXRSQY
- Anwar SM, Majid M, Qayyum A, et al. Medical image analysis using convolutional neural networks: a review. Journal of Medical Systems. 2018;42(11):226. doi: 10.1007/s10916-018-1088-1 EDN: ZTZIEH
- Miranda J, Horvat N, Fonseca GM, et al. Current status and future perspectives of radiomics in hepatocellular carcinoma. World Journal of Gastroenterology. 2023;29(1):43–60. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i1.43 EDN: QDGABL
- Kocak B, Akinci D’Antonoli T, Mercaldo N, et al. Methodological radiomics score (METRICS): a quality scoring tool for radiomics research endorsed by EUSUMII. Insights into Imaging. 2024;15(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s13244-023-01572-w EDN: CINMDC
- Aghakhanyan G, Filidei T, Febi M, et al. Advancing pediatric sarcomas through radiomics: a systematic review and prospective assessment using radiomics quality score (RQS) and methodological radiomics score (METRICS). Diagnostics. 2024;14(8):832. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14080832 EDN: GFBZWJ
Дополнительные файлы