Markers of viral hepatitis E (Hepeviridae, Orthohepevirus, Orthohepevirus A) in the imported Old World monkeys
- Authors: Dogadov D.I.1, Korzaya L.I.1, Kyuregyan K.K.2,3, Karlsen A.A.2,3, Mikhailov M.I.2,3
-
Affiliations:
- FSBRI «Research Institute of Medical Primatology» of the Ministry of Education and Science of Russia
- FSBRI «I.I. Mechnikov Research Institute of Vaccines and Sera»
- FSBEI FPE «Russian Medical Academy of Continuous Professional Education» of the Ministry of Health of Russia
- Issue: Vol 66, No 3 (2021)
- Pages: 182-188
- Section: ORIGINAL RESEARCHES
- URL: https://journal-vniispk.ru/0507-4088/article/view/118158
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.36233/0507-4088-34
- ID: 118158
Cite item
Full Text
Abstract
Introduction. Viral hepatitis E is a zooanthroponotic disease that occurs in humans and various animals, including monkeys. It is caused by hepatitis E virus (HEV) (Hepeviridae, Orthohepevirus: Orthohepevirus A), for which 8 genotypes have been described to date. Among them, strains of genotypes 1 and 2 have been isolated from humans, strains of genotypes 3 and 4 from humans and animals, and strains of genotypes 5–8 from animals only. The main threat of the disease is associated with the documented zoonotic transmission of HEV genotypes 3, 4, 7, and 8, to humans through infected meat, blood and milk. Thus, monkeys could be involved in the transmission of HEV.
The aim of this work was to study serological and molecular genetic markers of HEV infection in strepsirrhines (Old World monkeys, Cercopithecoidea), imported to the Adler Primate Center from various regions of the world (Tanzania, Vietnam, Mauritius).
Material and methods. Fecal (n = 224) and blood serum samples (n = 395) from cynomolgus (Macaca fascicularis) and vervet monkeys (Chlorocebus pygerythrus) were examined by the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR).
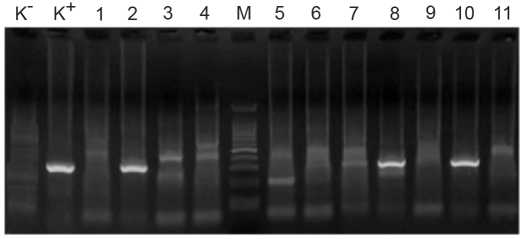
Results and discussion. The data obtained show the high detection rate (51.8%) of IgG antibodies to HEV among 5 groups of cynomolgus monkeys imported from Vietnam, with a predominance of highly reactive sera (84%). High detection rate of IgM antibodies in these animals (10.4%) was observed, with the large number of IgM-reactive sera in one particular group of animals (36.8%). The fact of detection of HEV RNA in two groups of cynomolgus monkeys (11.9% and 5.7%) is of particular importance. All HEV sequences of isolated from monkeys belonged to genotype 4.
Conclusion. Our data indicate that monkeys (in particular, cynomolgus monkeys) can serve as a natural reservoir of HEV genotype 4 for humans. This requires an appropriate set of anti-epidemic measures in a number of situations.
Keywords
Full Text
##article.viewOnOriginalSite##About the authors
D. I. Dogadov
FSBRI «Research Institute of Medical Primatology» of the Ministry of Education and Science of Russia
Author for correspondence.
Email: dima_loko86@mail.ru
ORCID iD: 0000-0003-1596-0509
Dmitriy I. Dogadov, Ph.D. (Biol.), Researcher of the Laboratory of Infection Virology.
354376, Sochi
Russian FederationL. I. Korzaya
FSBRI «Research Institute of Medical Primatology» of the Ministry of Education and Science of Russia
ORCID iD: 0000-0003-2259-5773
354376, Sochi
Russian FederationK. K. Kyuregyan
FSBRI «I.I. Mechnikov Research Institute of Vaccines and Sera»; FSBEI FPE «Russian Medical Academy of Continuous Professional Education» of the Ministry of Health of Russia
ORCID iD: 0000-0002-3599-117X
105064, Moscow
125993, Moscow
A. A. Karlsen
FSBRI «I.I. Mechnikov Research Institute of Vaccines and Sera»; FSBEI FPE «Russian Medical Academy of Continuous Professional Education» of the Ministry of Health of Russia
ORCID iD: 0000-0002-6013-7768
105064, Moscow
125993, Moscow
M. I. Mikhailov
FSBRI «I.I. Mechnikov Research Institute of Vaccines and Sera»; FSBEI FPE «Russian Medical Academy of Continuous Professional Education» of the Ministry of Health of Russia
ORCID iD: 0000-0002-6636-6801
105064, Moscow
125993, Moscow
References
- Bradley D.W. Enterically-transmitted non-A, non-B hepatitis. Br. Med. Bull. 1990; 46(2): 442–61. https://doi.org/10.1093/ oxfordjournals.bmb.a072409
- Matsuda H., Okada K., Takahashi K., Mishiro S. Severe hepatitis E virus infection after ingestion of uncooked liver from a wild boar. J. Infect. Dis. 2003; 188(6): 944. https://doi.org/10.1086/378074
- Spina A., Lenglet A., Beversluis D., de Jong M., Vernier L., Spencer C., et al. A large outbreak of Hepatitis E virus genotype 1 infection in an urban setting in Chad likely linked to household level transmission factors, 2016–2017. PLoS One. 2017; 12(11): 1–12. https://doi. org/10.1371/journal.pone.0188240
- Wang Y., Ling R., Erker J.C., Zhang H., Li H., Desai S., et al. A divergent genotype of hepatitis E virus in Chinese patients with acute hepatitis. J. Gen. Virol. 1999; 80(1): 169–77. https://doi. org/10.1099/0022-1317-80-1-169
- Smith D.B., Simmonds P., Izopet J., Oliveira-Filho E.F., Ulrich R.G., Johne R., et al. Proposed reference sequences for hepatitis E virus subtypes. J. Gen. Virol. 2016; 97(3): 537–42. https://doi. org/10.1099/jgv.0.000393
- Nan Y., Zhang Y.J. Molecular biology and infection of Hepatitis E virus. Front. Microbiol. 2016; (7): 1419. https://doi.org/10.3389/ fmicb.2016.01419
- Yamamoto H., Suzuki J., Matsuda A., Ishida T., Ami Y., Suzaki Y., et al. Hepatitis E Virus Outbreak in Monkey Facility, Japan. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012; 18(12): 2032–4. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid1812.120884
- Sridhar S., Teng J.L.L., Chiu T.H., Lau S.K.P., Woo P.C.Y. Hepatitis E virus genotypes and evolution: emergence of camel hepatitis E variants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017; 18(4): 1–19. https://doi.org/10.3390/ ijms18040869
- Mushahwar I.K. Hepatitis E virus: molecular virology, clinical features, diagnosis, transmission, epidemiology, and prevention. J. Med. Virol. 2008; 80(4): 646–58. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmv.21116
- Guu T.S.Y., Liub Z., Ye Q., Mata D.A., Li K., Yin C., et al. Structure of the hepatitis E virus-like particle suggests mechanisms for virus assembly and receptor binding. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2009; 106(31): 12992–7. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0904848106
- Hirano M., Ding X., Li T.C., Takeda N., Kawabata H., Koizumi N., et al. Evidence for widespread infection of hepatitis E virus among wild rats in Japan. Hepatol. Res. 2003; 27(1): 1–5. https://doi. org/10.3201/eid1808.120070
- Purcell R.H., Emerson S.U. Animal models of hepatitis A and E. ILAR J. 2001; 42(2): 161–77. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a031815
- Yamamoto H., Li T.C., Koshimoto C., Ito K., Kita M., Miyashita N., et al. Serological evidence for hepatitis E virus infection in laboratory monkeys and pigs in animal facilities in Japan. Exp. Anim. 2008; 57(4): 367–76. https://doi.org/10.1538/expanim.57.367
- Корзая Л.И., Кебурия В.В., Догадов Д.И., Лапин Б.А., Кюрегян К.К., Михайлов М.И. Маркёры гепатита Е у населения Большого Сочи и обезьян Адлерского приматологического центра. Вопросы вирусологии. 2016; 61(4): 176–80. https://doi. org/10.18821/0507-4088-2016-61-4-176-180
- Huang F., Yu W., Hua X., Jing S., Zeng W., He Z. Seroepidemiology and molecular characterization of Hepatitis E virus in Macaca Mulatta from a village in Yunnan, China, where infection with this virus is endemic. Hepat. Mon. 2011; 11(9): 745–9. https://doi. org/10.5812/kowsar.1735143X.730
- Корзая Л.И., Лапин Б.А., Кебурия В.В., Лазарева И.Я. Частота выявления антител к вирусу гепатита Е у обслуживающего персонала и у макак Адлерского питомника обезьян. Вопросы вирусологии. 2007; 52(1): 36–40.
- Yang F., Duan S., Guo Y., Li Y., Yoshizaki S., Takeda N., et al. Current status of hepatitis E virus infection at a rhesus monkey farm in China. Vet. Microbiol. 2019; 230: 244–8. https://doi. org/10.1016/j.vetmic.2019.01.021
- Корзая Л.И., Кебурия В.В., Гончаренко А.М., Догадов Д.И., Лапин Б.А. Маркёры вирусных инфекций у лабораторных приматов. В кн.: Материалы второй международной научной конференции «Фундаментальные и прикладные аспекты медицинской приматологии». Сочи; 2011: 79–88.
- Михайлов М.И., Малинникова Е.Ю., Кюрегян К.К., Исаева О.В. Случай завоза вируса гепатита Е 4 генотипа в Россию. Журнал микробиологии, эпидемиологии и иммунобиологии. 2016; 93(3): 64–9. https://doi.org/10.36233/0372-9311-2016-3-64-69
- Dogadov D.I., Korzaya L.I., Kyuregyan K.K., Karlsen A.A., Kichatova V.S., Potemkin I.A., et al. Natural infection of captive cynomolgus monkeys (Macaca fascicularis) with hepatitis E virus genotype 4. Arch. Virol. 2019; 164(10): 2515–8. https://doi. org/10.1007/s00705-019-04337-3
- Михайлов М.И., Кюрегян К.К., Малинникова Е.Ю., Исаева О.В., Карлсен А.А., Потёмкин И.А., и др. Вирусные гепатиты: прогнозы и проблемы. Эпидемиология и инфекционные болезни. Актуальные вопросы. 2019; 9(1): 71–80. https://doi.org/10.18565/ epidem.2019.9.1.71-80
Supplementary files