Том 33, № 2 (2025)
- Год: 2025
- Выпуск опубликован: 30.06.2025
- Статей: 10
- URL: https://journal-vniispk.ru/2413-1407/issue/view/17769
Весь выпуск
Региональная и отраслевая экономика
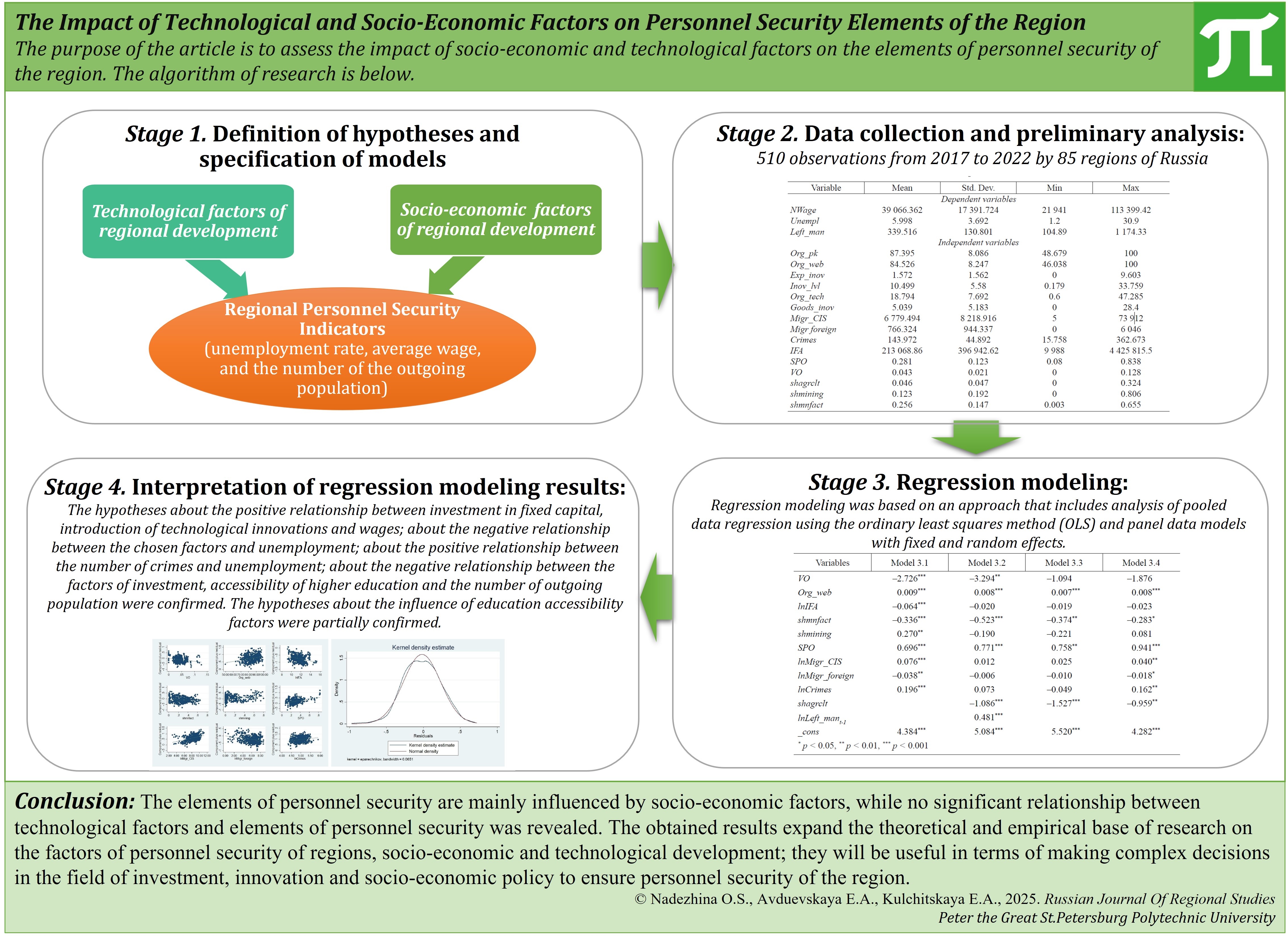
Влияние технологических и социально-экономических факторов на элементы кадровой безопасности региона
Аннотация
Введение. В условиях нестабильности регионы сталкиваются с проблемами оттока населения, снижения качества трудовых ресурсов, растущим дисбалансом на рынках труда. Решение этих системных проблем приобретает стратегическое значение для поддержания кадровой и национальной безопасности в целом. Разработка эффективных механизмов обеспечения кадровой безопасности региона невозможна без объективной оценки его резервов на основе экономико-математического моделирования. В силу относительной новизны категории «кадровая безопасность региона» в отечественной научной литературе не представлены исследования на данных субъектов Российской Федерации о взаимосвязях показателей технологического и социально-экономического развития с индикаторами кадровой безопасности, что ограничивает возможность выработки обоснованных рекомендаций для управления региональными системами в условиях современных кадровых и демографических вызовов. Целью статьи является оценка влияния социально-экономических и технологических факторов на элементы кадровой безопасности региона.
Материалы и методы. Материалом исследования послужили статистические данные о социально-экономическом и технологическом развитии 85 субъектов Российской Федерации за период с 2017 по 2022 год. Основным методом работы выступает регрессионный анализ. Использованы метод сквозной регрессии и методы панельных данных с фиксированными и случайными эффектами. На основе литературного обзора отобраны зависимые переменные – элементы кадровой безопасности (заработная плата, уровень безработицы и количество выбывшего населения) и сформулированы шесть гипотез о взаимосвязи названных переменных с технологическими и социально-экономическими факторами регионального развития.
Результаты исследования. Подтверждены гипотезы о положительной взаимосвязи инвестиций в основной капитал, внедрения технологических инноваций и заработной платы; количества преступлений и безработицы; об отрицательной взаимосвязи факторов социально-экономического и технологического развития с безработицей; факторов инвестиций, доступности высшего образования и количества выбывшего населения. Гипотезы о взаимосвязи элементов кадровой безопасности и факторов доступности образования были подтверждены частично.
Обсуждение и заключение. На элементы кадровой безопасности в основном влияют социально-экономические факторы, в то время как существенной взаимосвязи технологических факторов и элементов кадровой безопасности выявлено не было. Полученные результаты расширяют теоретическую и эмпирическую базу исследований о факторах обеспечения кадровой безопасности регионов, социально-экономического и технологического развития; будут полезны в части принятия комплексных решений в области инвестиционной, инновационной и социально-экономической политики в интересах укрепления кадровой безопасности региона.
 186 - 205
186 - 205


Основные ценовые и неценовые факторы развития возобновляемых источников энергии в странах Евросоюза
Аннотация
Введение. Рассматриваются основные факторы развития возобновляемых источников энергии (ВИЭ) в странах Европейского союза (ЕС), которые на современном этапе являются передовыми в данной области. Актуальность изучения ВИЭ определяется, с одной стороны, важностью охраны окружающей среды в рамках глобальной климатической повестки, с другой – недостаточным освещением названной темы в науке. Цель исследования состоит в определении основных ценовых и неценовых факторов, обеспечивающих развитие ВИЭ в странах ЕС; гипотеза заключается в том, что волатильность цен на углеводороды и импорт ЕС традиционных источников энергии из России выступает важным фактором развития ВИЭ в странах ЕС.
Материалы и методы. Возможные факторы влияния выделены по методологии PESTEL. Их сбор производился в рамках экспертной оценки современных трендов из открытых источников. На основе отобранного материала была построена полулогарифмическая линейная регрессия, оценивающая зависимость доли используемых ВИЭ страной ЕС от выделенных факторов в пределах 2019–2023 гг.
Результаты исследования. Согласно построенной модели, являются значимыми: уровень коррупции, индекс зеленого роста, дамми-переменная, которая иллюстрирует наличие национальной правовой базы в области зеленой энергетики, и количество выбросов парниковых газов на душу населения – на уровне 1 %; количество выпущенных страной «зеленых» облигаций – 5 %; цены на углеводороды, государственные расходы на научно-исследовательские работы (НИР) – на уровне 10 %. Гипотеза исследования подтверждена частично: цены на углеводороды представляют собой важный фактор, однако не ключевой, в то время как волатильность импорта ЕС традиционных источников энергии из России в рамках модели не значима.
Обсуждение и заключение. Разработка национального законодательства в сфере ВИЭ, финансирование научных проектов, актуализация зеленой повестки в гражданском обществе при низком уровне коррупции обеспечат твердую почву для развития технологий ВИЭ в странах ЕС. Результаты настоящего исследования могут быть полезны при подготовке государственными учреждениями стратегии использования ВИЭ в России, а также в рамках рассмотрения вопросов развития ВИЭ в ЕС, интеграции ЕС и Евразийского экономического союза (ЕАЭС).
 206 - 220
206 - 220


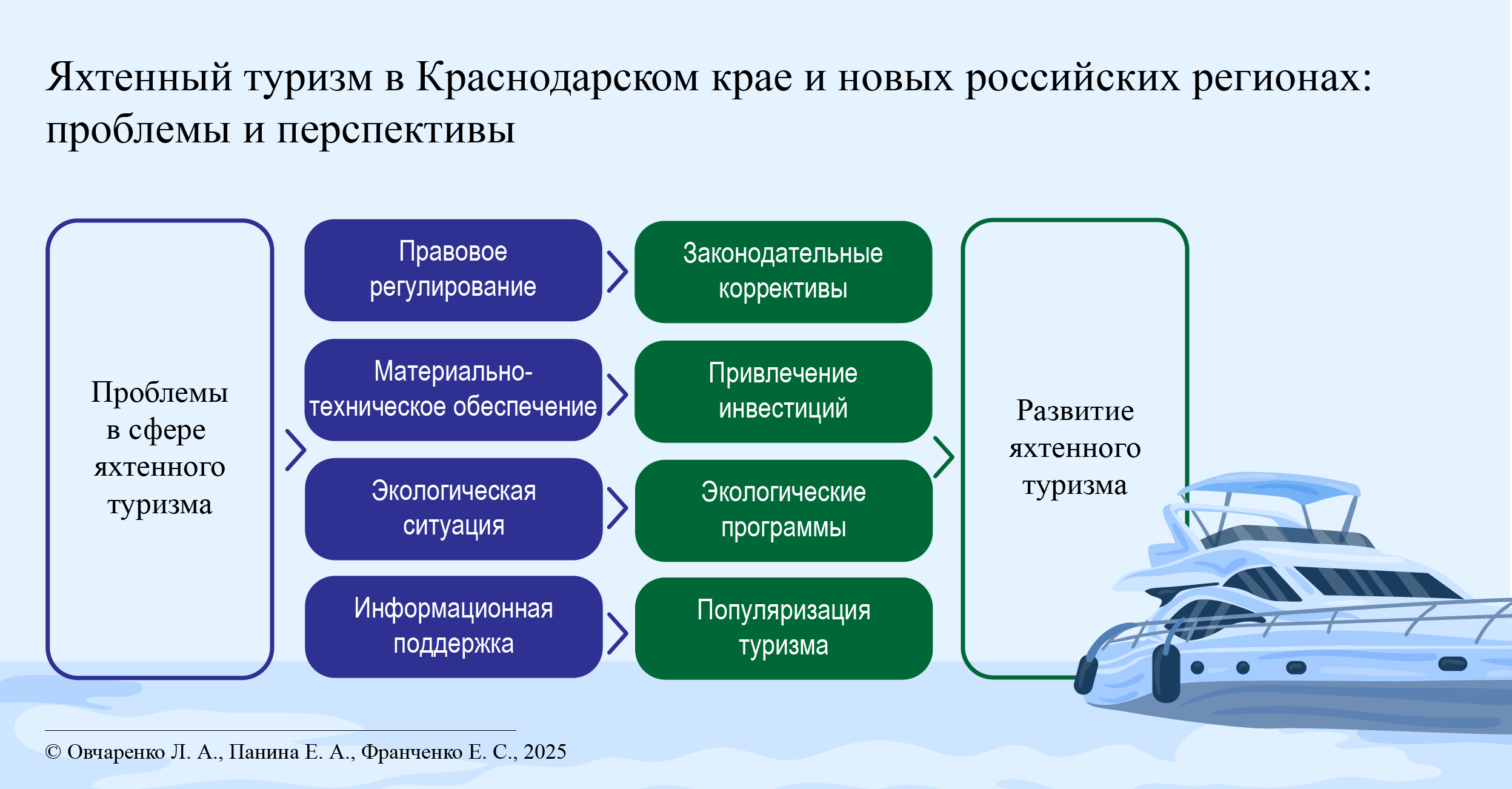
Яхтенный туризм в Краснодарском крае и новых российских регионах: проблемы и перспективы
Аннотация
Введение. Яхтенный туризм является перспективным видом туризма в Российской Федерации, о чем свидетельствует возросший за последние годы спрос на подобные путешествия. В ряде российских регионов спрос на внутренний яхтенный отдых превышает предложение, что объясняется пока еще имеющимися сложностями в развитии яхтенной инфраструктуры. В последнее время наблюдается тенденция повышения туристского интереса к морской акватории Краснодарского края как перспективному региону в сфере яхтенного туризма, а также новым российским регионам – Донецкой, Херсонской, Запорожской областям. Данное обстоятельство обусловлено тенденцией стратегического развития Азово-Черноморского побережья, а именно строительством марин, портоубежищ, топливных заправочных станций, туристсткой инфраструктуры и др. Строящаяся яхтенная инфраструктура автоматически притягивает в сферу туризма инвесторов в гостинично-ресторанный секторы, пляжный, активный виды отдыха, оживляет туристский потенциал регионов и способствует его экономическому развитию. Перед отечественной наукой стоит важная задача, связанная с необходимостью научно-методического обоснования перспективных инструментов функционирования яхтенного туризма, практическое воплощение которых позволит обеспечить формирование новых туристских кластеров, интегрирующих яхтенную инфраструктуру. Это будет содействовать соответствию яхтенной инфраструктуры Азово-Черноморского побережья темпам роста туристского интереса к данному виду туризма, проектированию базы для продвижения новых туристских направлений. Цель статьи – выявить проблемы и обосновать перспективы развития яхтенного туризма в Краснодарском крае и в новых российских регионах в пределах Азово-Черноморского побережья, обусловленные реализацией новых инвестиционных проектов яхтенной инфраструктуры.
Материалы и методы. Исследование базируется данных яхт-клубов и компаний, специализирующихся на обслуживании, аренде яхт, продаже яхтенного оборудования и маломерных судов, организации яхтенных круизов: «Storm crew», «International Yacht Training Worldwide», «Mediterranean Yacht Charter». Проведен SWOT-анализ привлекательности Краснодарского края, новых российских приазовских регионов для активного развития яхтенного туризма, на основе которого выделены конкурентные преимущества перечисленных регионов, способствующие активизации популярности и улучшению инвестиционного климата в данных территориях; обобщение и описание сведений, полученных эмпирическим путем, наглядное представление данных.
Результаты исследования. Уточнены понятия яхтенного туризма и яхтинга с учетом имеющихся теоретических подходов и мировой практики; выявлены проблемы, затрудняющие развитие яхтенного туризма в Краснодарском крае и в новых российских регионах; определен потенциал яхтенного туризма для развития и продвижения брендинга территорий; перечислены ключевые факторы активизации развития яхтенного туризма, которые должны стать импульсом его продвижения на российский и международный уровни с целью придания прибрежным территориям особого инвестиционного статуса.
Обсуждение и заключение. В Краснодарском крае и новых приазовских российских регионах неэффективность яхтенного туризма связана созданием на недостаточном уровне благоприятных условий инвестирования в развитие данного сектора, а именно созданием необходимой инфраструктуры, удовлетворяющей возросший интерес россиян к внутреннему туризму за счет сокращения потока выезжающих с целью яхтенных путешествий за рубеж. Функционирование яхтенного чартерного бизнеса, в основном, осуществляется за счет малого и среднего предпринимательства, которое финансово ограничено. Поэтому необходимо создать нормально работающие механизмы государственно-частного партнерства с целью инвестирования капиталоемких объектов яхтенной инфраструктуры, создать профессиональную систему обучения управляющих яхтенной инфраструктурой, привлечения яхтсменов. Туристическая сфера, в том числе яхтенная, в новых российских приазовских регионах будет активно развиваться по мере налаживания на данных территориях безопасной и мирной жизни. Данное исследование может быть использовано для совершенствования и корректировки процесса модернизации яхтенной индустрии регионов, субъектов туристской деятельности и государственного регулирования экономического развития территорий.
 221 - 238
221 - 238


Экономическая социология
Миграция предпринимателей из регионов России в Калининградскую область: возможности и ограничения использования их потенциала
Аннотация
Введение. Калининградская область остается миграционно привлекательным регионом России, несмотря на усиление после 2022 г. рисков и угроз. Для российского эксклава, где сформировалась активная предпринимательская среда, значительный научный интерес представляет изучение мигрантов-предпринимателей, открывающих новый или релоцирующих существующий бизнес. Цель настоящей работы состоит в исследовании миграции предпринимателей в Калининградскую область с точки зрения расширения использования их потенциала, что имеет высокую практическую значимость для роста вовлеченности внутренних мигрантов в экономику региона.
Материалы и методы. Работа основана на результатах социологических исследований, проведенных в 2022 и 2024 гг. в Калининградской области. В рамках репрезентативного опроса населения (1005 чел.) отобраны и изучены миграционные настроения предпринимателей (89 чел.). Выборка репрезентирует жителей региона по полу и возрасту, типу населенного пункта (городской/сельский). С использованием метода глубинных интервью выявлены стратегии миграции предпринимателей (13 чел.) в область из других регионов России. Пул информантов формировался методом снежного кома; отбор осуществлялся по сферам, наиболее привлекательным для внутренних мигрантов-предпринимателей.
Результаты исследования. Определены миграционные настроения, а также факторы притяжения и выталкивания; оценены возможности и ограничения реализации потенциала мигрантов-предпринимателей. Доказано, что совокупность выталкивающих и притягивающих факторов зависит от индивидуальных и средовых характеристик, миграционного и предпринимательского опыта, финансовых возможностей. Установлено, что для опрошенных предпринимателей, самозанятых и руководителей организаций региона характерна высокая миграционная подвижность, при этом настрой на смену места жительства представлен слабо. Выделены и обоснованы ключевые стратегии миграции предпринимателей: 1) выбор наилучших условий для бизнеса, 2) улучшение условий проживания, 3) творческий порыв. Разработаны рекомендации по росту вовлеченности внутренних мигрантов в экономику региона для наиболее полной реализации их предпринимательского потенциала.
Обсуждение и заключение. В соответствии с выделенными стратегиями миграции предложены и обсуждаются требуемые меры и механизмы поддержки бизнеса, которые могут способствовать более активному использованию потенциала предпринимателей и снятию ограничений в расширении их проектов. Результаты работы могут быть полезны при подготовке направлений реализации региональной политики по привлечению внутренних мигрантов в Калининградскую область, что имеет как теоретическую, так и практическую значимость. Перспективы дальнейших исследований связаны с изучением склонности внутренних мигрантов к предпринимательству в сравнении с местным населением
 239 - 256
239 - 256


Влияние институциональной среды на процессы международной трудовой миграции в регионы Российской Федерации
Аннотация
Введение. Актуальность темы исследования обусловлена возрастающей ролью международной трудовой миграции в социально-экономическом развитии регионов России и необходимостью эффективного управления потоками переселенцев. В условиях демографического спада и дефицита трудовых ресурсов привлечение иностранных мигрантов становится важным фактором экономического роста. Изучение детерминант международной трудовой миграции часто фокусировалось на социально-экономических характеристиках пунктов назначения. В данной статье рассматривается влияние качества государственного управления территориями на их способность привлекать трудовых иммигрантов.
Материалы и методы. Эмпирической базой исследования выступают сведения Росстата, а также информация Атласа «Исламское сообщество Российской Федерации»; основным методом – регрессионный анализ панельных данных (модель с фиксированными эффектами).
Результаты исследования. Статистическая обработка данных показала, что субъекты РФ с более высоким качеством государственного управления привлекают больше международных трудовых мигрантов. При этом большинство социально-экономических факторов, которые традиционно используются для объяснения привлекательности территории назначения, не получили подтверждения, хотя они косвенно входят в категорию «государственная состоятельность». Регрессионный анализ продемонстрировал положительное влияние доли мусульманского населения регионов РФ на численность (в относительном выражении) иностранных трудовых мигрантов. Концепция этнических сетей не прошла эмпирическую проверку.
Обсуждение и заключение. Международные трудовые мигранты предпочитают приезжать на территорию назначения с более высоким качеством государственного управления. В то же время важно обеспечивать социальную интеграцию иммигрантов и защиту их прав, чтобы избежать проблем в принимающем обществе, которые связаны с социокультурными различиями. Результаты исследования могут способствовать росту эффективности управления миграционными процессами на национальном и субнациональном уровнях, а также позволяют прогнозировать направления миграционного потока.
 257 - 270
257 - 270


Особенности подбора персонала: интеллектуальный анализ текстов резюме и вакансий
Аннотация
Введение. Рассматриваются особенности подбора персонала на российском рынке труда с акцентом на проблеме дисбаланса между требованиями работодателей и ожиданиями соискателей. В фокусе внимания – различия в репрезентации запросов сторон, позволяющие систематизировать кадровые потребности экономики через призму компетенций и трудовых обязанностей. Актуальность исследования обусловлена низкой сопряженностью взаимодействия субъектов рынка труда в условиях цифровизации, что порождает системные сбои в поиске работы и подборе кадров. Между тем данная тематика редко становится предметом социологического анализа и недостаточно представлена в научном поле.
Материалы и методы. Разработана авторская методика анализа больших данных рынка труда на основе 5 347 805 текстов резюме и вакансий, собранных на трех крупнейших российских платформах в 2019–2023 гг. Для обработки данных применялись алгоритмы NLP (Natural Language Processing), включая тематическое моделирование и кластеризацию, что позволило создать две иерархические таксономии: 55 параметров компетентности и 423 группы должностных обязанностей. Статистический анализ реализован методами описательной статистики, корреляционного анализа и моделирования временны́х рядов.
Результаты исследования. Эмпирический анализ выявил устойчивую информационную асимметрию между работодателями и соискателями. Стороны демонстрируют недостаточное понимание функционального назначения ключевых разделов объявлений о работе (компетенций и должностных обязанностей). Соискатели склонны указывать больше параметров компетентности, чем требуется работодателями, что указывает на гипертрофированное представление о рыночном спросе. Наблюдается рост интереса работодателей к отдельным группам должностных обязанностей, несмотря на это формулировки вакансий сохраняют общий характер, контрастирующий с детализацией специализированного опыта в резюме.
Обсуждение и заключение. Проанализирована степень сопряженности запросов субъектов рынка труда, акцентированы текущие и будущие дисбалансы между параметрами спроса и предложения. Определено, что рынок труда функционирует в условиях ограниченной рациональности. Тексты объявлений выполняют различные функции в зависимости от интерпретации сторонами. Параметры компетенций и должностные обязанности в вакансиях и резюме не согласованы, что приводит к длительным и неэффективным процессам отбора кандидатов. Результаты исследования могут быть использованы для разработки рекомендаций по оптимизации текстов о поиске работы и подборе персонала
 271 - 293
271 - 293


Социальная структура, социальные институты и процессы
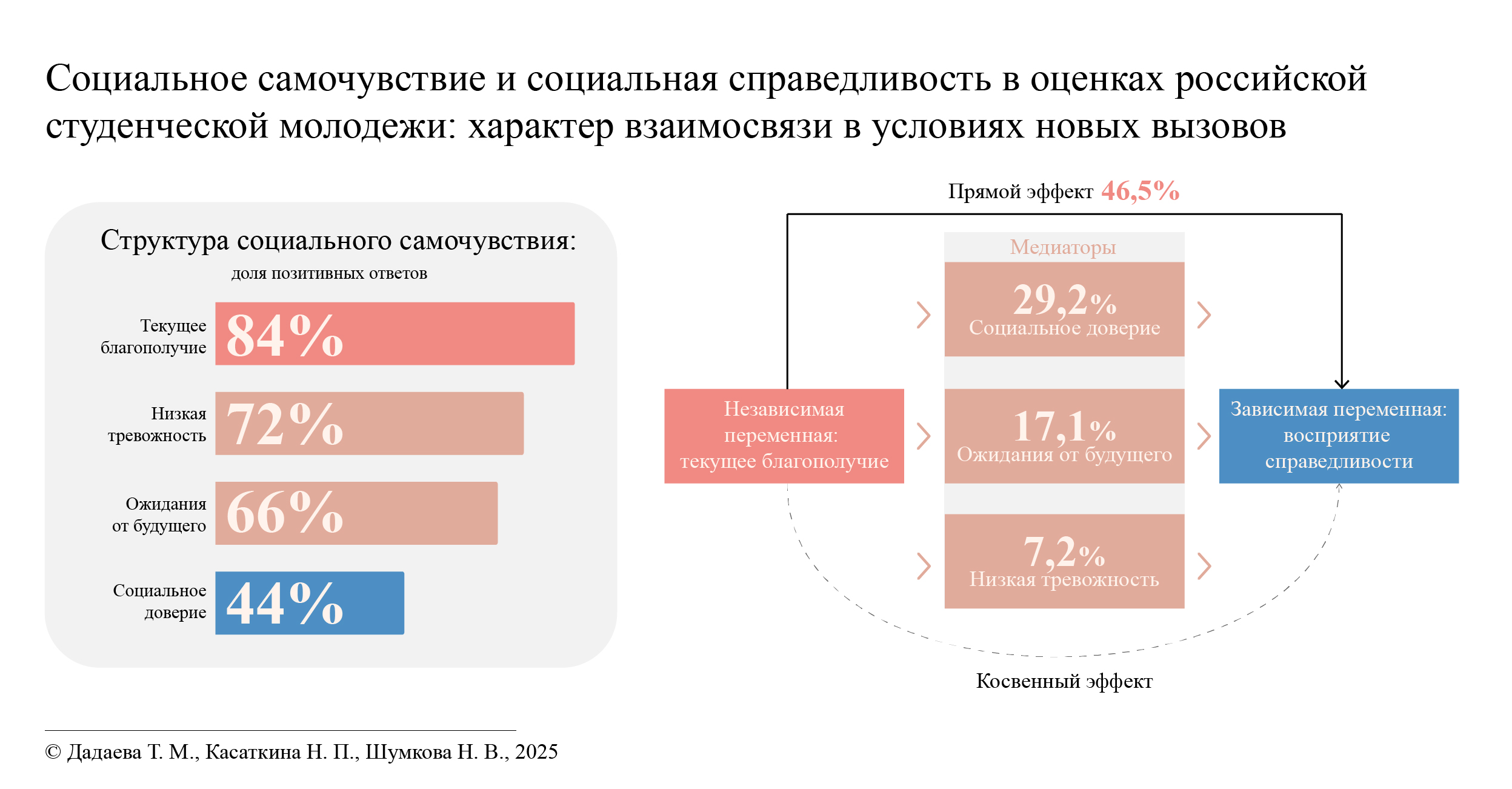
Социальное самочувствие и социальная справедливость в оценках российской студенческой молодежи: характер взаимосвязи в условиях новых вызовов
Аннотация
Введение. Обращение к теме социального самочувствия и восприятия социальной справедливости студенческой молодежью России актуализировано влиянием регионального неравенства (включая качество жизни) на жизненные траектории названной категории населения, потенциальными рисками социальной напряженности, а также недостаточной изученностью опосредующих механизмов взаимосвязи данных конструктов. Цель исследования – проанализировать компоненты социального самочувствия и характер их связи с представлениями о социальной справедливости у российских студентов в контексте региональных особенностей.
Материалы и методы. Проведено онлайн-анкетирование (октябрь-ноябрь 2024 г., n = 1 209 студентов дневных отделений вузов) в четырех регионах с разным качеством жизни: Московской области, Татарстане, Мордовии, Калмыкии. Социальное самочувствие измерялось через индексы текущего благополучия, ожиданий от будущего, социального доверия и тревожности. Удовлетворенность социальной справедливостью оценивалась по 5-балльной шкале. Использовались дескриптивная статистика, корреляционный анализ, линейная регрессия и тест Собеля для анализа медиации.
Результаты исследования. Сводный индекс социального самочувствия студенческой молодежи показал поляризацию: 54 % респондентов отнесены к категориям «хорошее»/«отличное» самочувствие, 18 % – к «плохое». В структуре социального самочувствия доминируют позитивные оценки текущего благополучия (84 %), в то же время социальное доверие демонстрирует более низкие показатели (44 %). Выявлена сильная положительная корреляция между субъективным благополучием и восприятием социальной справедливости (ρ = 0,63; p < 0,001). Регрессионная модель (R² = 0,216; p < 0,001) подтвердила влияние социального доверия (β = 0,220), тест Собеля – его опосредующую роль (29,2 % влияния). Региональная дифференциация нормативных представлений о справедливости коррелирует с объективным качеством жизни в регионах и социальным самочувствием студенческой молодежи.
Обсуждение и заключение. Подтверждена связь социального самочувствия и восприятия справедливости. Низкий уровень социального самочувствия у 18 % молодежи и региональные различия актуализируют проблемы укрепления социального доверия, адресной поддержки уязвимых категорий студенческой молодежи и учета территориальной специфики. Перспективно изучение взаимосвязи социального самочувствия и представлений о справедливости в лонгитюдных исследованиях.
 294 - 315
294 - 315


«Свои» и «чужие»: внутренние мигранты в представлениях жителей сибирских городов (на примере Иркутска, Красноярска и Томска)
Аннотация
Введение. Исследуется процесс формирования гражданской идентичности в современной России, рассматриваемый в контексте проблемы производства и преодоления границ между воображаемыми сообществами. Большинство существующих исследований сфокусированы на том, как трансграничная миграция влияет на переосмысление принимающим сообществом своей идентичности. При этом внутренние мигранты, являясь частью того же общества, могут воздействовать на идентификацию «мы-группы» внутри страны. Изучение этого вопроса важно для понимания конфигурации общегражданской идентичности и ее структуры с точки зрения поддержания и сохранения социальной солидарности. Цель работы состоит в выявлении механизмов, на основе которых представители «мы-группы» выстраивают границы в отношении внутренних мигрантов, а также в изучении проницаемости этих границ. Проанализировано влияние процессов внутренней миграции на представления жителей трех сибирских городов о «своих» и «чужих».
Материалы и методы. Материалом исследования послужили данные девяти фокус-групп с жителями Иркутска, Красноярска и Томска в возрасте 18–36 лет, проведенных в 2023 г. Респонденты набирались методом снежного кома. Информация обрабатывалась с помощью тематического осевого кодирования, выполненного в программе MAХQDA-2020, а также дискурс-анализа.
Результаты исследования. Установлено, что респонденты рассматривают и внутренних, и трансграничных мигрантов в качестве людей, попадающих в разрывы плотной сети коммуникаций, интегрированность в которую выступает основным признаком отнесенности к «мы-группе» носителей общегражданской идентичности. Внутренняя миграция способствует выстраиванию границ между местными и приезжими на локальном уровне. Коммуникация горожан и выходцев из сельской местности характеризуется сбоями, которые и служат для местного населения главной причиной исключения приезжих. Однако проницаемость границ по отношению ко внутренним мигрантам выглядит более явной, нежели по отношению к трансграничным. Исследование подтверждает, что главными факторами интеграции переселенцев в принимающую группу становятся включенность в локальные социальные сети и навыки использования городской среды.
Обсуждение и заключение. Внутренние мигранты могут преодолеть разрыв с принимающим обществом гораздо быстрее, нежели трансграничные, что подтверждает тезис об укреплении общегражданской идентичности в России. Возникающие коммуникативные сбои, однако, несут в себе конфликтный потенциал и угрозу социальной солидарности. В связи с этим результаты исследования могут быть полезны при разработке мер в сфере миграционной политики, поскольку актуализируют ключевые проблемы, решение которых в дальнейшем становится стратегической задачей.
 316 - 334
316 - 334


Социология культуры
Культурная мобилизация в период проведения специальной военной операции: как «новая» этика меняет «старые» привычки
Аннотация
Введение. В России после начала специальной военной операции (СВО) на Украине ускорились масштабные трансформации, затронувшие все сферы деятельности, в том числе практики культурного потребления. Ряд персон, занятых в креативных профессиях, публично поддержали или, напротив, осудили происходящее, что повлияло на их восприятие представителями власти и согражданами. Однако отношение к авторам и исполнителям тесно взаимосвязано с отношением к объектам культурного потребления, которые они производят. Данное исследование предпринято с целью выяснить, каким образом меняются (и меняются ли) культурные предпочтения людей (на уровне отдельно взятого региона) в период проведения СВО. Необходимость и значимость работы обусловлена как появлением нового ракурса проблемы культурного потребления, связанного с СВО, так и малочисленностью исследований на эту тему.
Материалы и методы. Исследование проводилось с сентября по ноябрь 2024 г. в Республике Мордовия методом анкетирования, реализуемого на платформе «Яндекс. Формы». Всего было опрошено 370 жителей региона из более чем 80 населенных пунктов. Квотная выборка репрезентирует население по полу, возрасту и месту проживания. Исследование носит разведывательный характер.
Результаты исследования. В условиях ведения СВО большинство опрошенных сохранили культурные предпочтения; каждый четвертый заявил об их изменении. Менее устойчивые практики культурного потребления характерны для людей старшего возраста, пенсионеров с низким доходом; более устойчивые – для молодежи, проживающей в столице региона, а также для лиц с высоким уровнем образования и доходов. Выделены три кластера, позволяющих идентифицировать участников исследования в зависимости от их отношения к текущей ситуации в сфере культурного потребления: либеральный, конформистский и консервативный. Либеральный объединяет выступающих против цензуры и излишнего государственного контроля. В консервативном кластере представлены сторонники разумных ограничений свободы слова, необходимости поддерживать деятелей, демонстрирующих патриотические убеждения, и отменять тех, кто признан иностранным агентом (иноагентом). Конформистский кластер составили респонденты с наименее устойчивыми привычками культурного потребления, ориентированные на те нарративы, которые связаны с сохранением и воспроизводством традиционных ценностей и продвигаются государством.
Обсуждение и заключение. Культурное потребление коррелирует с уровнем экономического и культурного институционализированного капитала. Изменения культурного потребления в условиях напряженности происходят преимущественно по признаку совпадения или несовпадения политических убеждений потребителя и производителя культурного продукта. Наиболее значимый фактор, влияющий на культурное потребление в условиях ведения СВО, – официальная информационная повестка, транслируемая государством. Полученные результаты могут быть полезны для управленцев, ответственных за формирование и реализацию культурной политики.
 335 - 353
335 - 353


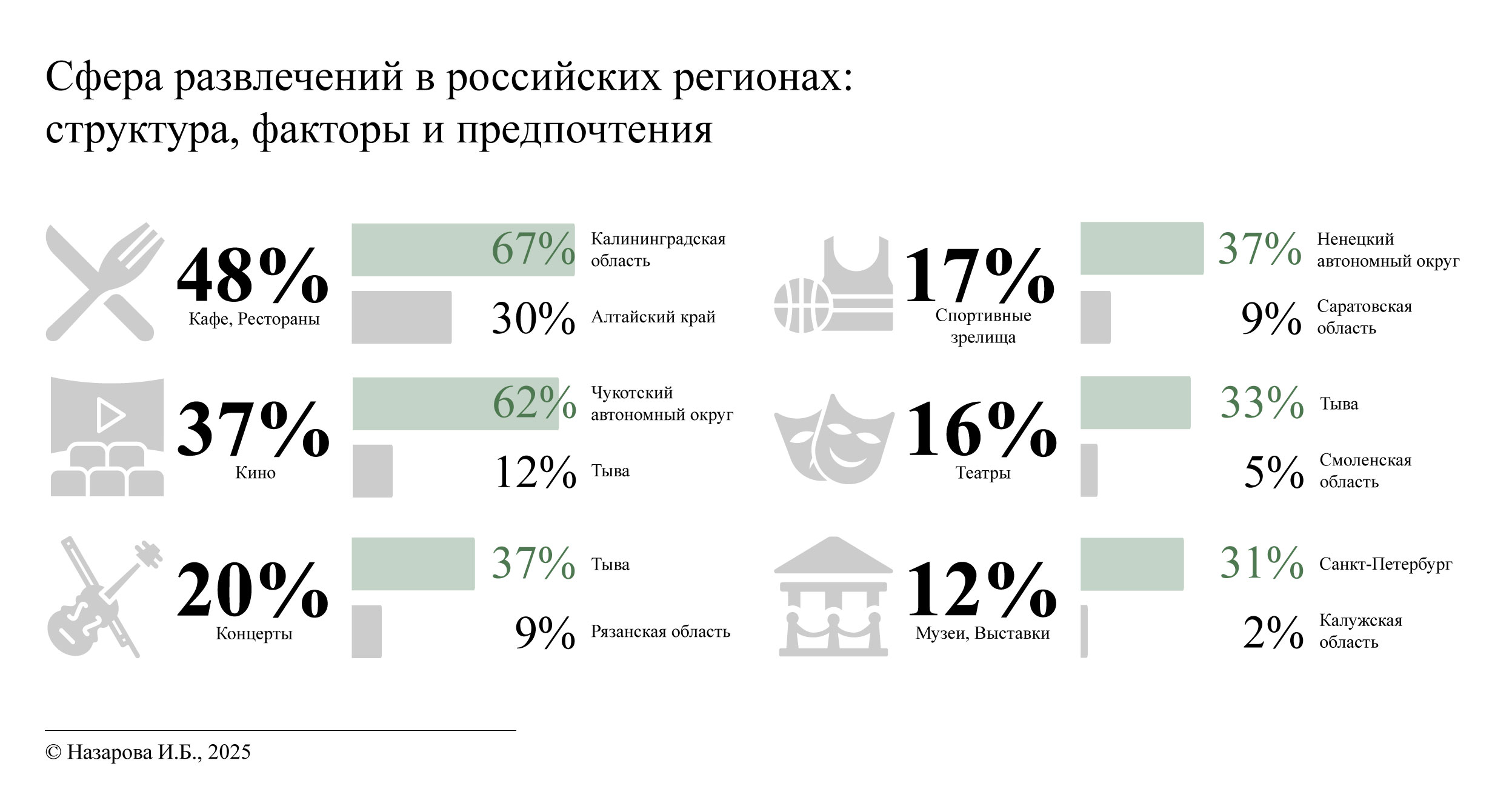
Сфера развлечений в российских регионах: структура, факторы и предпочтения
Аннотация
Введение. Развлечения играют большую роль в современном образе жизни, выступая важной составляющей досуга и благополучия. Несмотря на их значимость, комплексные исследования потребления развлечений в России остаются ограниченными. Данная работа призвана восполнить этот пробел. Проанализирована структура предпочтений в сфере развлечений среди жителей страны с акцентом на социально-демографических и региональных различиях.
Материалы и методы. В исследовании использованы сведения Комплексного наблюдения условий жизни населения (КОУЖ) за 2022 г., проведенного Росстатом, с охватом 117 634 респондентов в возрасте от 15 лет и старше. Для анализа тенденций и взаимосвязей применялись статистические методы, включая корреляцию Спирмена. Сравнение данных за 2018 и 2020 гг. позволило оценить восстановление после пандемии и долгосрочные изменения в потреблении развлечений.
Результаты исследования. Наиболее популярные виды развлечений: посещение ресторанов/кафе (48 %) и кинотеатров (37 %). Гендерные и возрастные различия значимы: молодежь чаще выбирает кино (73 %), женщины – театры (21 %), мужчины преобладают среди зрителей на спортивных мероприятиях (24 %). Городские жители активнее участвуют в культурной жизни (ходят в театры, музеи) по сравнению с сельским населением. Ярко выражены региональные различия: Чукотка (62 % посещаемости кино) и Санкт-Петербург (33 % посещаемости театров) представляют крайние значения.
Обсуждение и заключение. Выводы работы свидетельствуют о влиянии цифровизации, урбанизации и социально-экономических факторов на выбор развлечений. Если городская инфраструктура поддерживает разнообразие досуговых возможностей, то сельские районы сталкиваются с проблемами доступности. Результаты подчеркивают необходимость целенаправленной культурной политики для устранения региональных диспропорций. Ограничения связаны с исключением некоторых видов развлечений из набора данных КОУЖ и отсутствием данных качественных исследований.
 354 - 368
354 - 368