Vol 32, No 4 (2024)
- Year: 2024
- Published: 23.12.2024
- Articles: 10
- URL: https://journal-vniispk.ru/2413-1407/issue/view/16986
Full Issue
Public Administration and Sectoral Policies
Regulation and Characteristics of Reserving Budget Funds in Russian Regions
Abstract
Introduction. The relevance is due to the fact that very little attention is paid to this topic in domestic papers despite the importance of reserving budget funds as an instrument of countercyclical policy and sustainability of regional development. The purpose of the study is to identify the peculiarities of reserve funds regulation in the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, which will allow a better understanding of the motivation and incentives of the authorities and their risk management activities.
Materials and Methods. With the help of general scientific methods the analysis of regional laws on reserve fund and budget process and profile governmental resolutions for each subject of the Russian Federation was carried out, the original database on the main features of reserve funds at the regional level in Russia was created. This made it possible to systematize disparate information on various aspects of budget reserves in Russian regions, highlight common features and peculiarities – a step towards improving the institution of reserving funds to ensure regional financial stability.
Results. The main features and differences between the reserve fund of the subject of the Russian Federation as a public legal entity and the reserve fund (funds) of the executive authority of the subject are identified. It has been established that the reserve fund of the subject of the Russian Federation as a public legal entity is provided for by legislation in not more than half of the regions of the Russian Federation, while the reserve fund of the executive authority operates in every subject. The sources of the funds are, as a rule, a sharp increase in tax and non-tax revenues during the year and the balance on accounts at the beginning of the year. Areas of expenditures from the fund are usually limited and universal, but depending on the conditions of a particular region they can be diverse.
Discussion and Conclusion. The reserve fund of the subject of the Russian Federation remains an unpopular instrument. Unlike the reserve fund of the executive authority, its formation is not necessary, and there is no and spending of funds in the regions. The practical implication consists in the possibility of supplementing the measures of the federal policy of financial stability, as well as in the use of the presented results at the level of a regional administration regarding the experience of other regions in terms of regulation and the practice of formation and of reserve funds.
 618-634
618-634


Circular Economy in Agricultural Production: Potential for Implementation in New Institutional Conditions
Abstract
Introduction. The concept of circular agricultural production is a promising trend for ensuring food security and reducing current negative environmental effects. The aim of the study is to analyse the prospects for the development of a circular economy in the agricultural sector of the Krasnodar Territory in the new institutional environment.
Materials and Methods. The research process used the methods of critical analysis of modern literature, analysis of official statistical data, regulatory and programme documents that form the institutional framework for the development of closed-loop economy in agriculture. The main regulatory and program documents influencing the current and future institutional transformations of a circular economy in agriculture and the valorization of generated agricultural waste are analyzed.
Results. The differential characteristics of the concept of circular agricultural production are determined; the basic principles and limitations of a circular economy in agriculture are highlighted, as well as the benefits and costs of a circular transition in agriculture. Some specific characteristics of agricultural production in Krasnodar Territory are described, which determine the priority of implementing circular practices.
Discussion and Conclusions. It has been revealed that the emerging model for managing the circular transition in agricultural production in our country has a “top-down” character with the determining role of governmental institutions. This model has both undeniable advantages and areas of deficiency. The transformation of the characteristics of this model will occur under the influence of the specific characteristics of Russian regions. The results of the study are important for executive authorities and business structures for the institutional design of the introduction of circular economy in the agricultural sector of the Krasnodar Territory and other agricultural regions.
 635-652
635-652


Sociology of Management
Communication of Local Governments and the Population in Social Media: Regions of the Ural Federal District
Abstract
Introduction. The relevance of the topic is determined by the need for a practical solution to the problem of communication assessment of local government bodies with the population in social media. The lack of an effective methodology for such an assessment and its results increases the importance of this work. The purpose of the article is to analyse the success of communication of the executive authorities of the municipal entities of the Ural Federal District with the population on the official pages of the social network “VKontakte” and to offer the success index.
Materials and Methods. The authors used the database of official accounts of municipal, municipal district and municipal area administrations (n = 203) and heads of corresponding municipalities (n = 198) of the regions of the Urals Federal District in the social network “VKontakte”. The data were collected using the parsing tool Cerebro 3.0; the data were analyzed using both standard indicators of social network analysis and those proposed by the authors. The index method was used to summarize the data. This approach made it possible to systematize and aggregate heterogeneous information in order to compare the objects of analysis.
Results. The authors have developed and tested on the materials of the regions of the Urals Federal District a methodology for calculating the index of success of communication between local governments and the population in the social network “VKontakte”. It has also been demonstrated that higher publication activity does not unequivocally lead to more successful communication outcomes. It is revealed that in most cases, municipalities with small populations are the most successful communicators. It is noted that subscriber engagement is higher in the accounts of heads of municipalities compared to the accounts of municipal administrations.
Discussion and Conclusion. The authors’ proposed methodology for assessing the success of local government communications helps to identify the most successful practices, differentiate municipalities and regions. The index allows to go from evaluation of information openness to analysis of content published and recommendations on how to what content is needed to be more successful in communicating with the public. The results of the study will be useful for state and municipal employees involved in communication with the public.
 653-672
653-672


Traditionalism in China’s State Governance: Regional Specificity
Abstract
Introduction. The relevance of the study is due to the increasing importance and influence of global and, at the same time, regional processes on the process of governance. The purpose of the article is to identify the regional specifics of traditionalism as a systemic phenomenon in the processes of state governance in China; in this case, we consider China as a region participating in global and transregional relations.
Materials and Methods. The study is based on sociologist R. Redfield’s concept of social organization tradition, which distinguished between “big” and “small” traditions, and the adaptation of this concept in Chinese sociology. In order to identify the relationship between traditionalism and Chinese specificity of public administration in their historical aspect and to determine the current region-specific trends of traditionalism’s influence on public administration, scientific studies of Chinese sociologists were analyzed.
Results. In particular, the systemic characteristics of traditionalism are examined along two interrelated dimensions: philosophical, which determines the value orientations of society, and practical, which aims to ensure stable social interaction. Special attention is paid to the “great state tradition”, which in modern Asia with China as an example manifests itself in the adaptation of traditional management concepts to modern conditions. The processes of penetration of traditional values into political discourse and ideology are studied, emphasizing that modern traditionalism is not a return to the past, but a tool for searching for arguments in the past to actualize modern managment concepts.
Discussion and conclusion. The regional specificity of state governance is largely determined by the “big state tradition”, which remains a significant factor of the governance system in China, influences the “little tradition” and seeks ways to adapt to it. The practical significance of the article lies in the possibility of using its results in planning interaction with administrative departments and public structures of the PRC.
 673-690
673-690


Regional and Sectoral Economy
The Impact of Economic Diversification on Labor Productivity in Russian Regions
Abstract
Introduction. Achieving national goals requires reducing the dependence on commodity exports based on the diversification of the economic structure, which has its own characteristics in regions with different industrial specialization, having a different impact on labor productivity. The purpose of the article is to determine the impact of diversification of the regional sectoral structure on the level and dynamics of labor productivity in the regions.
Materials and Methods. In the first block, the impact of economic diversification on the dynamics of labor productivity and economic activity in the regions was assessed. I. In the second block, the assessment of the impact of the development of regional of types of economic activities of specialization and types of economic activities of the reserve of specialization was carried out by assessing the levels of labor productivity, innovation activity and export orientation of types of economic activities. The structural and sectoral typology of regions was used to form differentiated proposals on regional policy priorities.
Results. The estimates obtained for 2010‒2021 showed the absence of a pronounced rigid relationship between the nature of changes in labor productivity and the level of economic diversification in Russia’s regions: geographically differentiated combinations of them were identified, which determines the need for a selective approach to determining the priorities of state support for regions.
Discussion and Conclusion. The practical implementation of the study should be the clarification of the priorities of the state regional policy to support the effective diversificationof of the economy of the Russian regions based on the accelerated development of their new specialized industries with high levels of innovation activity and export orientation. The prospects of the study are related to the substantiation of specific mechanisms to support the advanced development of a complex of high-tech types of economic activity in the regions.
 691-711
691-711


Tourism Opportunities for Residents of the Russian Arctic: Within the Region, in Russia and Abroad
Abstract
Introduction. Russian Arctic regions have a significant tourism potential, but it is not fully realized. The purpose of the study is to assess the possibilities of the population of the Arctic regions of the Russian Federation to realize tourism in their places of residence, in Russia and abroad.
Materials and Methods. The research methodology is based on the authors’ approach to the analysis of nine Arctic regions of the Russian Federation. The approach allows to fully evaluate and compare with average Russian values the tourism opportunities of the population of the regions of the Arctic zone in their places of permanent residence and beyond. The analysis of tourism opportunities was carried out on the basis of indicators divided into four semantic blocks: economic and social indicators, transport infrastructure, accommodation infrastructure and leisure and entertainment infrastructure. Summary scores for four groups of indicators were calculated based on cluster analysis using the k-means method as well as minimax normalization.
Results. The study revealed a significant gap in the Arctic regions of the Russian Federation in terms of economic and social indicators of the population, transportation connectivity and the level of development of infrastructure for accommodation, leisure and entertainment. Limited tourism opportunities for residents of the Arctic regions were identified. The worst situation is observed in the Nenets Autonomous Area, somewhat better in the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia).
Discussion and Conclusion. The resuits indicate the need for integrated development of the Arctic regions. The article is of scientific and practical significance for scientists working on tourism development in the Arctic, regional authorities, representatives of the tourism industry.
 712-732
712-732


Experience of Legal Regulation of Management of Other People’s Business in Different Regions of the World
Abstract
Introduction. In the context of economic sanctions from unfriendly countries, our country has taken a course on deoffshorization of the economy ‒ return of private capital from foreign and international financial structures (trust funds) and their transfer into the Russian legal field. The purpose of the study is to carry out a comparative analysis of the legal regulation of foreign business management in foreign countries in search of best practices for implementation in Russian law.
Materials and Methods. Comparative-legal and comparative-historical approaches were used. The analysis of scientific works, legislative and regulatory documents related to the issues of management of other people’s property in other countries was carried out, as well as examples of law enforcement practice were generalized. With the help of methods of comparative jurisprudence, system analysis, legal modeling the differences in approaches to business management through trust funds and trust agreements are revealed, the main principles of legal regulation of the management of other people’s property as an integral institution are determined, possible ways of reforming the Russian law are formulated.
Results. As a result of the analysis, it was concluded that modern foreign legal systems have developed a variety of models for managing private business assets. The trust model is developed in the United Kingdom, the United States and other common law countries. The legal systems of mixed and continental law have attempted to abandon the direct borrowing of trust and have developed various ways to introduce institutions similar to trust into their own legal systems (trust-like structures). At present, prerequisites have emerged in Russian law for the creation of separate legal regulation of relations on private property management, not identical to the institution of trust.
Discussion and Conclusion. In order to create a favorable investment climate in our country it is necessary to develop the institutions of professional management of other people’s business and inheritance business planning, in this regard it seems advisable to include in the Civil Code of the Russian Federation a special section regulating the management of private property. The obtained results have practical significance for representatives of the legal, economic, business community, practicing lawyers, teachers, as well as representatives of the lawmaking initiative.
 733-748
733-748


Social Structure, Social Institutes and Processes
Voluntary Activities of Student Youth in Condition of Modern Russian Society
Abstract
Introduction. The relevance of the research is conditioned by the presence of a sustainable institutional request of the authorities and the public sector regarding the development of youth civic potential. However, young people demonstrate an inert format of mobilisation of social activity resources. The aim of the study is to analyse the dynamic environment of student volunteer activity. Young people’s choices and evaluations of the content, scope and variety of voluntary activities shows obvious vectors of typical choice, resource uniqueness, and also demonstrates examples of a number of typological regional areas and topics.
Materials and Methods. The study used a systems approach and structural-functional analysis in order to substantiate the issue of regional student volunteering. . The basis for the analysis was the results of the authors’ own research on the topic: “Volunteer activity of student youth in Kuzbass” (n = 715), conducted in 2023–2024, reports on the implementation of volunteer projects in the Kemerovo region – Kuzbass for 2022.
Results. The implementation of volunteer activities in the region can be carried out in a consolidated manner or have multidirectional vectors for applying the activity and resource potential of student youth. The conditions of socio-political communication determine a certain dynamics, intensity, and temporality of volunteer activities. Analysis of the results of a questionnaire survey among young people revealed a contradiction: respondents offer recommendations for practical improvement in the organization of volunteer activities, but find it difficult to identify the subjects of implementation of these changes.
Discussion and Conclusion. Student volunteering is defined as an interaction that is built in the form of interactive multifunctional relationships, when the interests of the parties involved are interconnected in a combination of requests from the drivers of volunteering, stakeholders and experts, as well as the performers of the volunteer role themselves. The results obtained are of practical significance for volunteer organizers, regional supervisors, authorities, directly to regional volunteer communities and young people.
 749-767
749-767


Youth Social Selfie: Social Strategies of Regional Youth
Abstract
Introduction. The relevance of the article is determined by the need for monitoring control of indicators and elements of social strategies of youth in the conditions of high social risks of the border region. The purpose of the article is to determine the typical social characteristics of regional young people based on key indicators of their social strategies.
Materials and Methods. The article examines the results and analysis of the materials of the 2023 study conducted in the Belgorod region using an online survey of young people aged 14 to 35 years. The use of this method made it possible to cover a large number of respondents, including in hard-to-reach areas and settlements of the region, to ensure the representativeness of the sample. The study involved 5881 people (schoolchildren, students and working youth from the region). The purpose of the study was to determine the characteristics and indicators of the social strategies of young people.
Results. The result of the study was a social portrait of regional youth based on key types of strategic dispositions and life plans for 12 social strategies. Key potentials were identified related to career ambitions, orientation to traditional family values, desire for education and self-development, attention to one’s own health, and the need for self-realization. Risks that could seriously damage to regional human capital were identified: economic infantilism combined with high economic aspirations, social passivity and political egocentrism, situational (selective) spirituality, increased migration potential (orientation to leave the region).
Discussion and Conclusion. As a final conclusion, it is worth emphasizing the informational and analytical capabilities of the social portrait of regional youth based on social strategies: the features of the portrait allow us to determine the possibilities of future social investments of young people in the regions, to clarify the problems and deficiencies of socialization effects, and to formulate tasks to ensure the possibility of implementation of life plans of young people for state and municipal government bodies. The materials of the article may be in demand by state youth policy management bodies of various levels, state and municipal administration bodies, youth organizations and educational institutions.
 768-792
768-792


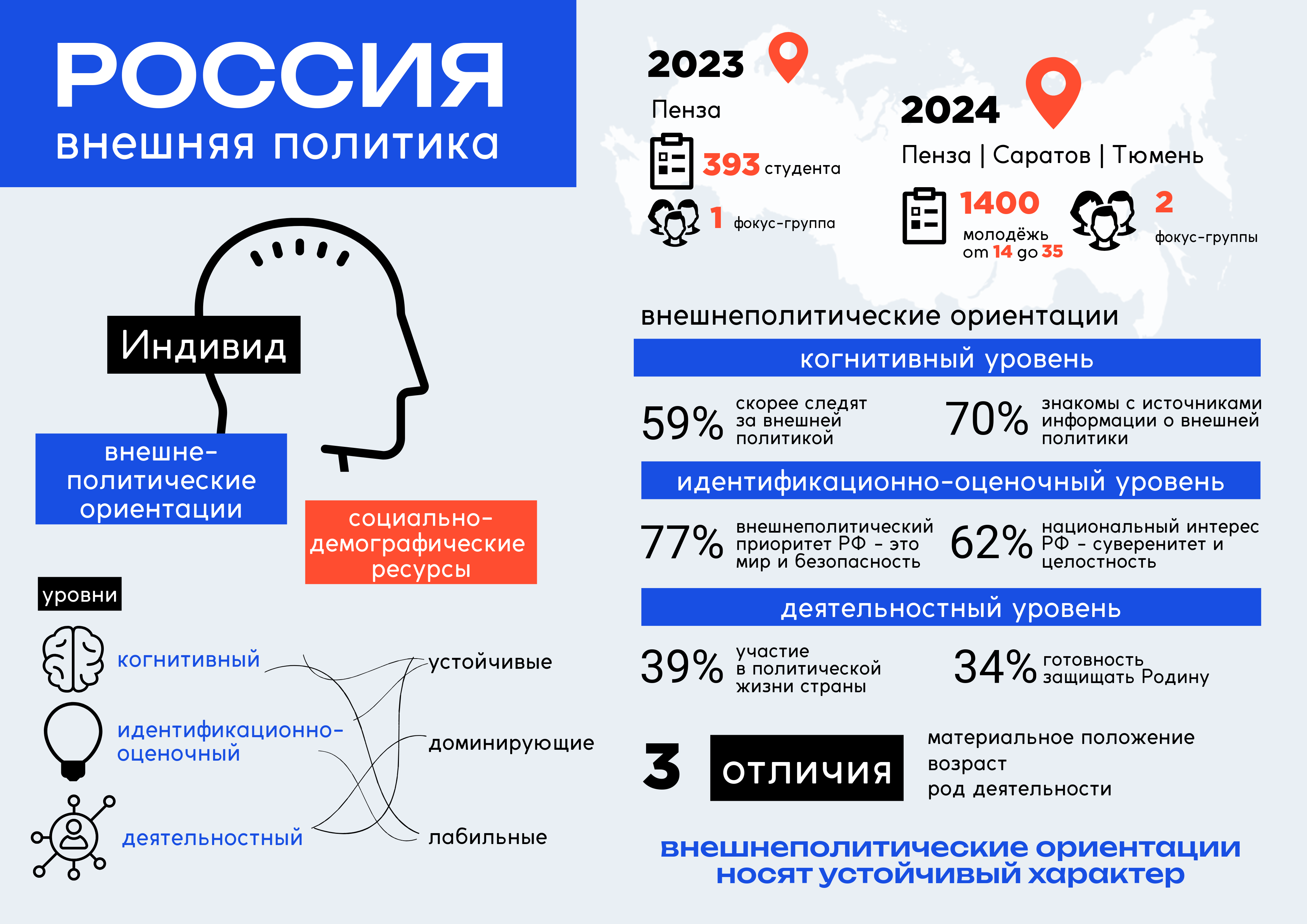
Modern Youth Foreign Policy Orientations in the Context of International Tension
Abstract
Introduction. The study of the peculiarities of foreign policy orientations of various social groups is of great importance for modern Russian society and requires comprehensive analysis in the context of the ongoing transformations of the world order and international tensions. The purpose of the research is to determine the structure and dynamics of foreign policy orientations of Russian youth in modern conditions.
Materials and Methods. Analysis of all-Russian surveys on similar topics was conducted; the results of quantitative and qualitative author’s studies conducted in 2023–2024 among youth of the Russian regions: Penza, Saratov and Tyumen regions were analyzed. This made it possible to identify the dominant foreign policy orientations of young people and reveal the degree of support for Russia’s political course in the international arena.
Results. The author’s structural model is presented, reflecting the essential content and main components of the system of foreign policy orientations of Russians, based on the Russian foreign policy approach at three levels: cognitive, identification-evaluation and activity. The author’s research allowed to obtain new data on the system and dominant foreign policy orientations, their direction and current dynamics; the similarity of foreign policy orientations of youth in different regions was determined and some of their differences in the socio-demographic section were revealed.
Discussion and Conclusion. The foreign policy orientations of modern young people are highly developed, which is reflected both at the cognitive and at the identification-evaluation level. A positive image of Russia has been formed in their consciousness; they fully share Russia’s leading role in the modern world order and demonstrate understanding and acceptance of the foreign policy decisions made. The obtained results can be used in improving the conceptual framework of youth policy and the system of civic education of modern youth.
 793-815
793-815